Panama Canal’s Water Crisis: A Climate Wake-Up Call for Global Trade and Local Communities
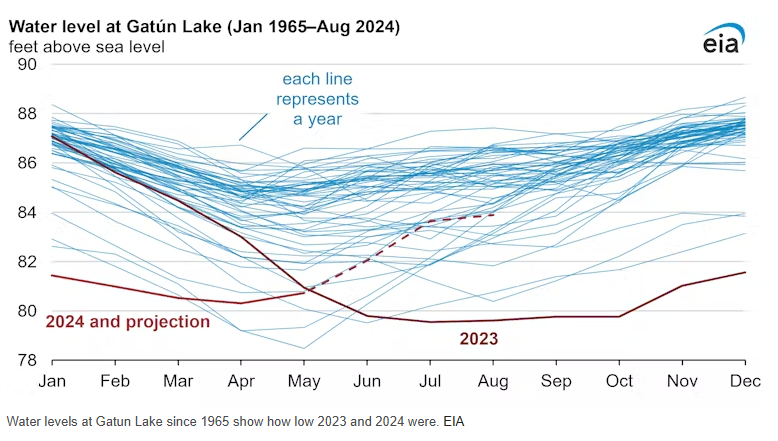
The Panama Canal, a critical artery for global trade, is grappling with an unprecedented water crisis. Prolonged droughts, intensified by climate change and El Niño events, have led to historically low water levels in Gatun Lake, the canal’s primary freshwater source. This shortage has forced authorities to reduce daily ship transits, causing significant delays and economic repercussions worldwide.

Key Points
Global Trade Disruptions
With about 7% of global trade passing through, the canal’s reduced capacity has led to increased shipping costs and rerouted cargo, impacting international supply chains.
Local Water Security
The same freshwater used for canal operations is vital for Panama’s population, agriculture, and hydropower. Drought conditions have heightened tensions over water allocation, affecting over 2 million residents.
Controversial Solutions
Plans to construct a new dam on the Indio River aim to secure water for the canal but would displace thousands and submerge communities, sparking social and environmental concerns.
This crisis underscores the urgent need for sustainable water management and climate adaptation strategies to safeguard both global commerce and local livelihoods.







